Hardware Trojans
Potential Targets#
- Consumer electronics
- Smartphones
- IoT
- Cars
- Planes
- Critical Infrastructure
- Power Grid
- Agriculture
- Water
- Military Applications
- Manufacturing
Crypto AG? - 1955#
- A signal intelligence company
- Provide tools for end-to-end encryption
- Super strong encryption used by 120 countries
- Except for
- NSA backdoors (as early as 1955)
- Possible hardware trojans
- International incident in Iran
Supermicro - 2018#
- Grain of rice sized chip
- According to Bloomberg
- Create a network backdoor into systems
- Government?
- AWS?
- Apple?
- Banks?
- Other?
- Foundry based attack
- Story never retracted
- Create a network backdoor into systems
- May have never happened
HP StorageWorks P2000 - 2010#
- Network storage device
- Enterprise solution
- Hardcoded backdoor
- User:
admin - Password:
guesses?
- User:
- What could this lead to?
German Backdoors - 2018#
- Recorded and sent ping to command and control server
- The device's phone number
- Location information, including longitude, latitude, and a street address
- IMEI identifier and Android ID
- Screen resolution
- Manufacturer, model, brand, OS version
- CPU information
- Network type
- MAC address
- RAM and ROM size
- SD card size
- Language and country
- Mobile phone service provider
- Stored in firmware makes it unremovable
Assurance Wireless - 2020#
- Discovered by Malware bytes
- Part of free/low-cost phone and data program
- Operated by Virgin Mobil
- Preinstalled with Chinese malware
- Software based malware
Lot's of Academic Work#
- Experiences in Hardware Trojan Design and Implementation (Jin et al. 2009)
- Hardware trojan design competition
- Sequential Hardware Trojan: Side-channel aware design and placement (Wang et al. 2011)
- Hard to test hardware trojan design
- On Hardware Trojan Design and Implementation at Register-Transfer Level (Zhang and Xu)
- Hard to detect by passive unused circuit techniques
- Silicon Demonstration of Hardware Trojan Design and Detection in Wireless Cryptographic ICs (Liu et al. 2016)
- Stealthy Wireless Key Extraction
- Stealthy Dopant-Level Hardware Trojan (Becker et al. 2013)
- PNP Trojan
Making it useful - targeting TRNG#
- TRNG is used for
- Secure web browsing
- Disk Encryption
- Cloud applications
- Uses multiple components
- Entropy source (TRNG) -> Digital Processing (AES) -> Crypto Key
- Needs 256 bits of entropy for crypto key ( keys)
- What if we fix 228 bits ( keys)
- Defense with scanning electron microscope
IC Fab Process#
- Design
- IP - licensed by third parties
- Models
- Tools - Cadence or similar
- Designers - Employees
- 3rd Party "Requests"
- Fabrication
- Mask generation
- Lithography
- Packaging
- Manufacturing test
- Shipping
- Which do you trust?
- Say you're Raytheon designing ICs for missiles, you have to trust your design engineers, fabricators, etc. If you don't trust anyone, you can't use the IC
Security Concept - Trusted Compute Base#
- Minimum set of tools, people, hardware, etc that you trust
- What is the TCB for an embedded system design?
- What is the TCB for a cloud designer?
- What is the TCB for an ASIC designer?
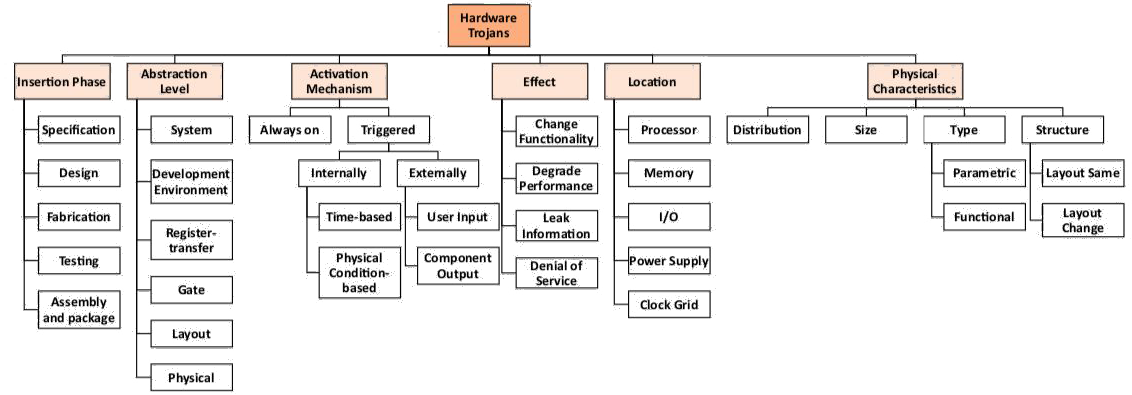
Current State of Design/Detection#
- Ad-hoc attacks
- Varying assumptions
- Ad-hoc metrics
Benchmarking Trojans#
- What is the benchmark
- Goal - set of standard tests for detection methods
- Set of standard metrics for test
- Limitation - only tests what we test for
Design Goals#
- Goal
- Stealthy
- Avoid test procedures
- Chooses triggers that won't happen during testing
- Use multiple triggers
- Sequence of triggers
- Select orthogonal triggr conditions
- Avoid useless circuit checking
- Avoid test procedures
- Controllable
- Stealthy
Don't Care#
- What is a don't care condition in digital design?
- Proof of concept design
- AES Implementation
- DC conditions matter when overclocked
- Allows for key transmission